
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps companies evaluate their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. This dual perspective is essential for conducting effective market opportunity assessments.
Applications of SWOT Analysis in Market Research
-
Identifying Market Positioning – Evaluate a company’s position in the market, identify its strengths and weaknesses, and understand how its products or services are perceived.
-
Competitor Analysis – Analyze competitors’ strengths and weaknesses to uncover market gaps and determine how the company can differentiate itself.
-
Assessing Market Opportunities – Evaluate the feasibility of entering new markets with new products, services, or segments.
-
Identifying and Mitigating Risks – Anticipate potential threats and develop strategies to mitigate them.
-
Strategic Planning – Use insights from SWOT analysis to inform strategic decisions and prioritize internal actions based on external opportunities.

Key Components of SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Strengths are internal factors that give a company a competitive edge, such as competitive pricing, a strong reputation, or low employee turnover.
How to Identify Strengths:
Focus on internal factors that provide a positive advantage and set the company apart. Evaluate core competencies where the company excels compared to competitors. Benchmarking can highlight areas of excellence, while brand reputation and performance metrics—like sales figures and profitability—offer tangible indicators. Customer feedback from surveys or reviews can also reveal key strengths.
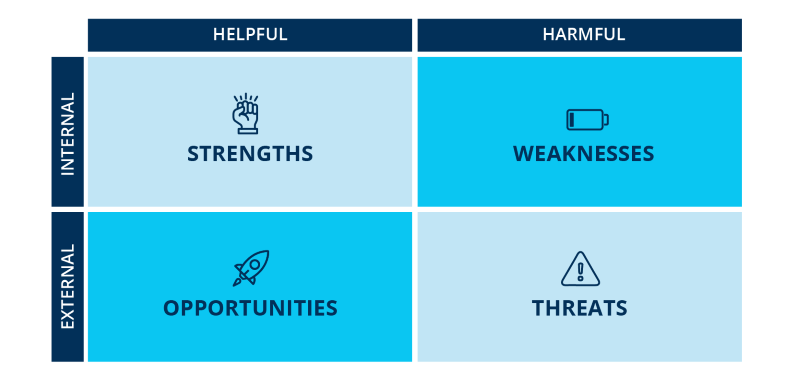
Weaknesses
Weaknesses are internal factors that hinder a company’s success, such as a weak brand, poor reputation, or subpar products.
How to Identify Weaknesses:
Identify internal areas where the company underperforms or lacks proficiency. Look for inefficiencies in processes or resources. Tangible weaknesses may be reflected in low sales, poor profitability, or negative customer feedback. Comparing performance with competitors can also highlight areas for improvement.

Opportunities
Opportunities are external factors that a company can leverage to its advantage, such as economic growth, emerging markets, or favorable regulations.
How to Identify Opportunities:
Conduct brainstorming sessions and external research to gather insights on competitors, market trends, and industry developments. Look for factors like competitor weaknesses, regulatory changes, or technological advancements. Also, consider how internal strengths or weaknesses might be leveraged or addressed to create new opportunities.

Threats
Threats are external factors that could negatively impact a company’s success, such as increased competition, economic downturns, or new regulations.
How to Identify Threats:
Use research and brainstorming to identify external risks in the market, industry, or competitive landscape. These may include strong competitors, unfavorable policies, or economic instability. Internal weaknesses can also become threats if left unaddressed.
Readers of this article also viewed:
How to Measure Brand Performance with the Brand Health Wheel The Value Equivalence Framework: A Simple but Powerful Questioning Technique PESTLE Analysis: Understanding Market Influences for Better Decision-Making Using the Push-Pull Model to Successfully Bring New Products to Market Competitive Landscape Analysis with Porter’s Five Forces Framework How to Apply the Three Circles Framework in Strategic B2B Research How Market Research Can Help Sharpen B2B Strategic Positioning
To discuss how our tailored insights programs can help solve your specific business challenges, get in touch and one of the team will be happy to help.

